Traditional Moroccan Medicine
July 14, 2014 Written by JP [Font too small?]In 1989, a review article in the World Health Forum defined the role of traditional health practices in modern day Morocco. The piece, authored by Dr. Jamal Bellakhdar, noted that, “Traditional medicine is still popular in Morocco since it is an important form of health care for many people”. He goes on say that, “Its positive aspects could be encouraged if it were officially recognized and given a place in the health system.” Now, some twenty-five years later, a slew of scientifically controlled studies have emerged which substantiate several of the historical remedies employed by Arab and Berber healers.
Argan oil and black cumin are arguably the two trendiest Moroccan supplements currently on the market. The former is frequently added to exotic hair and skin care formulas in the hopes of promoting a flawless complexion and lustrous hair. The latter is boldly described on one website as, “A Remedy for Everything but Death”. Wow! A third remedy common to Morocco is fenugreek seed. You’ll find it in everything from hair growth sprays to formulas and teas intended to increase breast milk production and muscle mass. Some of these claims are clearly exaggerated, if not completely unbelievable. Having said that, this should not dissuade you from considering these remedies altogether.
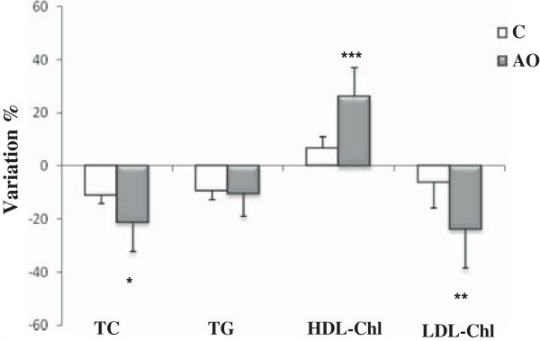
So, what is the truth about argan oil, black cumin and fenugreek? According to the latest batch of peer-reviewed studies, the internal use of argan oil genuinely affects the body in some pretty significant ways. Namely, argan oil supplementation (25 mL/day) improves various cardiovascular indices (HDL, LDL cholesterol, oxidative status and platelet aggregation) and increases luteinizing hormone and testosterone levels in men. Two trials reveal that black cumin, likewise, reduces risk factors associated with heart disease in both overweight and postmenopausal women. In addition, black cumin seed oil was recently found to safely correct sperm abnormalities, including poor morphology, motility and volume in infertile men. Finally, a review appearing in the January 2014 edition of Nutrition Journal, determined that fenugreek intake is capable of lowering both long and short term blood sugar in diabetics. What’s more, two other studies report that combining fenugreek with conventional medications for polycystic ovary syndrome and Parkinson’s disease enhances overall treatment outcomes. These are legitimate examples of age old, Moroccan remedies functioning quite nicely in the world of modern medicine.
Note: Please check out the “Comments & Updates” section of this blog – at the bottom of the page. You can find the latest research about this topic there!
To learn more about the studies referenced in today’s column, please click on the following links:
Study 1 – A New Look at Traditional Medicine In Morocco … (link)
Study 2 – Argan Oil Prevents Prothrombotic Complications By Lowering Lipid … (link)
Study 3 – Argan Oil and Postmenopausal Moroccan Women: Impact On the … (link)
Study 4 – Effect of Argan and Olive Oil Consumption On the Hormonal Profile … (link)
Study 5 – A Randomised Controlled Trial On Hypolipidemic Effects of Nigella … (link)
Study 6 – Effects of Nigella Sativa L. Seed Oil On Abnormal Semen Quality In … (link)
Study 7 – The Effects Of 8-Week Nigella Sativa Supplementation and Aerobic … (link)
Study 8 – Effect of Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum-Graecum L.) Intake On … (link)
Study 9 – Efficacy and Safety Of Standardized Extract Of Trigonella Foenum… (link)
Study 10 – Evaluation of Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum-Graceum L.), Effects … (link)
Argan Oil Intake Lowers Cardiovascular Risk Profile
Source: J Transl Med. 2014 Mar 31;12(1):82. (link)
Tags: Argan Oil, Black Cumin, Fenugreek
Posted in Alternative Therapies, Heart Health, Men's Health


July 14th, 2014 at 7:55 pm
Hi JP,
Thank you again for taking us along in your discoveries in remote countries of natural medicines that may be helpful to some of us!
Paul
July 15th, 2014 at 12:47 pm
I’m happy to do so, Paul! Thank you for your support!
Be well!
JP
August 11th, 2014 at 8:54 pm
Update: Black cumin oil may improve vitiligo:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4102993/
Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2014 Jun;16(6):e4515. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.4515. Epub 2014 Jun 5.
Comparing Nigella sativa Oil and Fish Oil in Treatment of Vitiligo.
Ghorbanibirgani A1, Khalili A1, Rokhafrooz D2.
BACKGROUND:
Vitiligo is one of the autoimmune skin diseases that destroy the melanocytes of the skin. Moreover, its prevalence varies in different countries and regions.
OBJECTIVES:
The aim of this study was to compare the effect of Nigella sativa and fish oil on vitiligo lesions of the patients referred to a dermatology clinic.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
This randomized, double blind clinical trial was conducted in the dermatology clinic of the Imam Khomeini Hospital Ahvaz, Iran, from June to December 2011. We used a randomized simple sampling. From 96 patients with vitiligo, 52 eligible patients were selected and allocated to two groups with equal size. The study medications were applied twice a day by patients on their lesions. After six months, the improvement rate of lesions was assessed by the Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (VASI). Data were analyzed using SPSS v. 15; P value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. RESULTS: After six months, a mean score of VASI decreased from 4.98 to 3.75 in patients applying topical Nigella sativa and from 4.98 to 4.62 in those using topical fish oil. Most of the percent improvement observed in upper extremities, trunk, head, and neck of those who received Nigella sativa and head, neck, trunk, and feet of those who received fish oil. No adverse effect was reported by the patients. CONCLUSIONS: Nigella sativa oil and fish oil were effective in reduction the size of patient's lesions; however, Nigella sativa was more effective in comparison to the fish oil. Therefore, using Nigella sativa with the major drugs in the treatment of vitiligo is recommended. Be well! JP
June 5th, 2015 at 1:41 pm
Update 06/05/15:
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/fo/c5fo00316d#!divAbstract
Food Funct. 2015 Jun 1.
Effects of Nigella sativa oil with a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women: a randomized controlled clinical trial.
Obesity is typically associated with increased risk factors of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Therefore, a therapeutic approach that aims to control body weight and metabolic profile might be effective in preventing CVDs. We aimed to determine the effects of Nigella Sativa (NS) oil with a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women. In this double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial, 90 obese women were recruited. Participants were females aged 25-50 years old with body mass index (BMI) between 30 and 35 kg m-2. They were randomly assigned to receive a low-calorie diet with 3 g per day (1 g before each meal) NS oil or placebo for 8 weeks. Anthropometric indices, dietary intake and biochemical parameters were measured at the baseline and after the intervention. Eighty-four females completed the trial (intervention n = 43, placebo n = 41). Two groups were similar in the baseline characteristics. After the intervention, dietary intake was changed in both groups compared to the baseline, but the differences were not significant between the two groups. In the NS group, weight (-6.0 vs. -3.6%; p < 0.01) and waist circumference (-6.9 vs. -3.4%; p < 0.01) decreased significantly compared with the placebo group at the end of the trial. Comparison of biochemical parameters presented a significant decline in triglyceride (-14.0 vs. 1.4%; p = 0.02) and very low density lipoprotein (-14.0 vs. 7%; p < 0.01) levels in the NS group compared to the placebo group. NS oil concurrent with a low-calorie diet can reduce cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women. However, more clinical trials are needed to elucidate efficacy of NS as a complementary therapy in obese subjects. Be well! JP
July 11th, 2015 at 2:25 pm
Update 07/11/15:
http://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/abs/10.1024/0300-9831/a000206?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3dpubmed
Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2014;84(3-4):196-205.
Effect of Fenugreek Seeds on Serum Metabolic Factors and Adiponectin Levels in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
This triple-blind randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted on 88 type 2 diabetic (T2DM) patients (males and females). Subjects in the fenugreek seed (n=44) and placebo (n=44) groups consumed 10 g/d of powdered whole fenugreek seeds or 5 g/d of wheat starch for 8 weeks. Fasting blood samples, anthropometric measurements and dietary records were collected at the baseline and at the end of the trial. Fenugreek seeds significantly decreased fasting blood glucose (P=0.007) and HbA1c (P=0.0001), serum levels of insulin (P=0.03), homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (P=0.004), total cholesterol (P=0.005) and triglycerides (P=0.0001) and increased serum levels of adiponectin (P=0.001) compared with placebo. No significant changes were shown in serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in both groups. In conclusion, fenugreek seeds improved glucose metabolism, serum lipid profile and adiponectin levels in studied subjects, and may be useful in the control of diabetes risk factors in TD2M patients.
Be well!
JP
September 22nd, 2015 at 8:56 am
Updated 09/22/15:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378874115301471
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 16.
Efficacy and safety of Honey based formulation of nigella sativa seed oil in functional dyspepsia: A double blind randomized controlled clinical trial.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: A honey based formulation from Nigella sativa L. (N. sativa) has been used in Traditional Persian Medicine for upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Considering the traditional use of this formulation and its ingredients known pharmacologic effects, this study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of N. sativa seed oil mixed with honey in treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia.
METHODS AND MATERIALS: Seventy patients diagnosed with functional dyspepsia according to ROME III criteria and confirmed by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy were selected to receive a traditional honey based formulation of Nigella sativa (5mlN. sativa oil orally daily) or placebo for 8 weeks in a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial using a parallel design with a 1:1 allocation ratio. Patients were evaluated prior to and following 8 weeks of the intervention in terms of the Hong Kong index of dyspepsia severity, presence of H. pylori infection based on urease test, scores in different domains of short form (SF-36) health survey, and any observed adverse events.
RESULTS: The mean scores of Hong Kong index of dyspepsia severity sores and the rate of H. pylori infection were significantly lower in the N. sativa group comparing the placebo group after the intervention (P<0.001). No serious adverse event was reported.
CONCLUSION: This study showed that adjuvant supplementation of honey based formulation of N. sativa can cause significant symptomatic improvement of patients with functional dyspepsia whom received the standard anti-secretory therapy. The results should be investigated further in studies with longer duration and larger sample size.
Be well!
JP
January 26th, 2016 at 4:14 pm
Updated 1/26/16:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/13685538.2015.1135323
Aging Male. 2016 Jan 20:1-9.
Testofen, a specialised Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract reduces age-related symptoms of androgen decrease, increases testosterone levels and improves sexual function in healthy aging males in a double-blind randomised clinical study.
This study examined the effect of Testofen, a specialised Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract on the symptoms of possible androgen deficiency, sexual function and serum androgen concentrations in healthy aging males. This was a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial involving 120 healthy men aged between 43 and 70 years of age. The active treatment was standardised Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract at a dose of 600 mg/day for 12 weeks. The primary outcome measure was the change in the Aging Male Symptom questionnaire (AMS), a measure of possible androgen deficiency symptoms; secondary outcome measures were sexual function and serum testosterone. There was a significant decrease in AMS score over time and between the active and placebo groups. Sexual function improved, including number of morning erections and frequency of sexual activity. Both total serum testosterone and free testosterone increased compared to placebo after 12 weeks of active treatment. Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract is a safe and effective treatment for reducing symptoms of possible androgen deficiency, improves sexual function and increases serum testosterone in healthy middle-aged and older men.
Be well!
JP
June 17th, 2016 at 1:20 pm
Updated 06/17/16:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4520377/
Prz Menopauzalny. 2014 Oct;13(5):280-8.
Skin hydration in postmenopausal women: argan oil benefit with oral and/or topical use.
THE AIM OF THIS STUDY: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of daily consumption and/or application of argan oil on skin hydration in postmenopausal women.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Sixty postmenopausal women consumed butter during the stabilization period and were randomly divided into two groups for the intervention period: the treatment group absorbed alimentary argan oil (n = 30) and the control group olive oil (n = 30). Both groups applied cosmetic argan oil in the left volar forearm during a sixty days’ period. Evaluation of skin hydration, i.e. transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and water content of the epidermis (WCE) on both volar forearms of the two groups, were performed during three visits at D0, D30 and after sixty days (D60) of oils treatment.
RESULTS: The consumption of argan oil has led to a significant decrease in TEWL (p = 0.023) and a significant increase in WCE (p = 0.001). The application of argan oil has led to a significant decrease in TEWL (p = 0.01) and a significant increase in WCE (p < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Our findings suggest that the daily consumption and application of argan oil have improved the skin hydration by restoring the barrier function and maintaining the water-holding capacity. Be well! JP
December 9th, 2016 at 2:42 pm
Updated 12/09/16:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27917705
Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2016 Dec 4.
Efficacy of Argane oil on metabolic syndrome in a Moroccan knee osteoarthritis population.
Five medical conditions characterizes metabolic syndrome: abdominal obesity, elevated blood pressure, elevated fasting plasma glucose, high serum triglycerides, and low high-density lipoproteins cholesterol. When a patient has three of the five above parameters, he is called to have metabolic syndrome, and these conditions represents a key element in cardiovascular diseases. On the other hand, knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease which was shown to be affected by some of the parameters of metabolic syndrome. Edible Argane oil is used in Moroccan folk medicine against several health conditions, such as knee osteoarthritis, though, evidence-based medical data about the above health benefit from Argane oil treatment are lacking. In the present clinical controlled study, we have found that consumption of Argane oil by 38 patients who have knee osteoarthritis and metabolic syndrome can improve several of their metabolic syndrome parameters and decrease their blood lipid atherogenic ratios. The present clinical study, to the best of our knowledge, is the first one to show that Argane oil consumption could be a therapeutic preventive tool against key cardiovascular risk factors of metabolic syndrome in knee osteoarthritis patients.
Be well!
JP
January 24th, 2017 at 12:57 pm
Updated 01/23/17:
http://www.medsci.org/v14p0058.htm
Int J Med Sci 2017; 14(1):58-66.
Efficacy of FurosapTM, a novel Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract, in Enhancing Testosterone Level and Improving Sperm Profile in Male Volunteers
Background: Dietary fiber rich fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds have exhibited cardioprotective, hypolipidemic and other health benefits. Furosap (FS), an innovative, patented, 20% protodioscin-enriched extract was developed in our laboratory from fenugreek seeds. This study examined the free and total testosterone levels, sperm profile and morphology, sexual health, mood and mental alertness, and broad spectrum safety parameters of FS in 50 male volunteers following supplementation over a period of 12 weeks.
Methods: Institutional Review Board (IRB) and other regulatory approvals were obtained for our study. This one-arm, open-labelled, multi-center study was conducted in 50 male volunteers (age: 35 to 65 years) over a period of 12 weeks to determine the efficacy of FS (500 mg/day/subject) on free and total testosterone levels, sperm profile, sperm morphology, libido and sexual health, mood and mental alertness, and broad spectrum safety parameters.
Results: Free testosterone levels were improved up to 46% in 90% of the study population. 85.4% of the study population showed improvements in sperm counts. Sperm morphology improved in 14.6% of volunteers. Majority of the subjects enrolled in the study demonstrated improvements in mental alertness and mood. Furthermore, cardiovascular health and libido were significantly improved. Extensive safety parameters were evaluated which included blood chemistry data. No significant changes were observed in serum lipid function, cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL and LDL levels, hemogram (CBC), hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity.
Conclusion: Overall, the results demonstrate that FS, enriched in 20% protodioscin, is safe and effective in attenuating testosterone levels, healthy sperm profile, mental alertness, cardiovascular health and overall performance in human subjects.
Be well!
JP
March 29th, 2017 at 11:30 am
Updated 03/29/17:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28344755
Electron Physician. 2016 Nov 25;8(11):3193-3197.
Effect of Topical Application of Nigella Sativa Oil and Oral Acetaminophen on Pain in Elderly with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Crossover Clinical Trial.
BACKGROUND: Limited evidence supports Nigella sativa’s role as an effective complementary and alternative medicine and the anti-inflammatory effects of Nigella sativa on patients with allergic rhinitis.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of topical application of Nigella sativa oil and oral acetaminophen on pain in the elderly with knee osteoarthritis residing in a parents’ home in Sabzevar.
METHODS: This study is done as a crossover clinical trial. After obtaining written consent of elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, they were randomly divided into two groups. In step 1, in group 1, 1 cc of Nigella sativa oil was applied on the knee joint every 8 hours for 3 weeks; for the second group, every 8 hours for 3 weeks, patients were given 1 tablet of 325 mg acetaminophen. After a period of 1 month without medication to wash out each group, in step 2, each treatment group received the drug interaction in the same way as above. Pain was determined using a visual scale (VAS) before and after the first and second stages. Treatment response was defined as a decrease in pain scores over 1.5. Data analysis was performed with an R software mixed model.
RESULTS: This study was done on 40 elderly patients: 18 (45%) men and 22 (55%) women. Their mean year and weight were 75.66±8.9 years and 69.67±14.33 kg, respectively. Study results showed that topical application of Nigella sativa oil and oral acetaminophen reduced pain in elderly with knee osteoarthritis; after using Nigella sativa oil, the reduction of pain was higher (p=0.01).
CONCLUSION: The results of this study showed that topical application of Nigella sativa oil was effective in reducing pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis; therefore, it is recommended as a safe supplement for these elderly.
Be well!
JP
March 25th, 2018 at 11:48 am
Updated 03/25/18:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1744388117302487
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice – Available online 22 March 2018
Purpose: This study has been carried out to investigate the analgesic effect of black cumin oil on individuals with knee pain.
Method: The experimental group (n = 30) and control group (n = 30) have been randomly selected. The control group patients have continued their routine prescription. For the experimental group, black cumin oil has been applied by rubbing to their knees 3 times a week for 1 month.:
Findings: As a result of the study, the mean VAS values of the patients in the experimental group has changed to 7.50 ± 0.97 on the 1st day and 6.30 ± 1.14 on the 30th day and there has been a significant decrease in pain severity in this group (p < 0.001). Results: This study has shown that the pain relieving properties of black cumin oil is effective on geriatric individuals living with knee pain. Be well! JP
February 16th, 2019 at 4:35 pm
Updated 02/16/19:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ptr.6313
Phytother Res. 2019 Feb 14.
The effect of cumin supplementation on metabolic profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized, triple blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a cluster of interconnected serious disorders, which is a major health problem whose prevalence is increasing. Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to the disease pathogenesis and its complications. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of Cuminum cyminum L. (which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties) essential oil (CuEO) supplementation on inflammatory and antioxidant status in patients with MetS. In this clinical trial, 56 patients with MetS aged 18-60 years received either 75-mg CuEO or placebo soft gel, thrice daily, for 8 weeks. Data on anthropometric parameters, food consumption, tumor necrosis factor alpha, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, catalase, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were assessed at the beginning and at the end of the study. Compared with the placebo group, CuEO increased SOD (149.17; 95% CI, [67.93, 230.42]), TAC (0.24; 95% CI, [0.09, 0.38]) and decreased MDA (-0.36; 95% CI, [-0.66, 0.06]), (p < 0.01). In within-group analysis, CuEO led to 13.3% decrease in MDA and 6.7% increase in TAC levels (p < 0.04). The results indicated that CuEO supplementation can improve some antioxidative indices, as SOD and TAC, while decreasing MDA in patients with MetS. Be well! JP