Hydrotherapy for Multiple Sclerosis
August 31, 2011 Written by JP [Font too small?]Recently, news of a major discovery in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS) research was presented in the journal Nature. An examination of 9,772 patients with MS and 17,376 “healthy” volunteers confirmed that 57 genes were associated with the disease. This finding should help MS specialists move closer to pinpointing a cause and eventually a cure. But, in the here and now those already living with MS need to be aware of safe treatments that are currently available.

Hydrotherapy, exercises conducted in swimming pools, is a therapeutic option that rarely makes headlines. Three studies published in the 2010 and 2011 argue that this healing modality deserves more attention. The international trials, conducted in Iran, Spain and the US, report that the regular practice of aquatic exercises can improve various measures of MS symptomatology including: depression, disability, fatigue, pain and spasms. The duration of the interventions ranged from 4 to 20 weeks. Two to three weekly sessions of hydrotherapy lasting 60 minutes each were required of the participants. As promising as these initial findings are, there may be a simple way to improve upon them. Of late, numerous studies have revealed a correlation between adequate sun exposure and MS. It appears that living in sunnier climates may interfere with the chief cause of MS incidence and progression known as demyelination. Also of interest is that this protective effect may be independent of sun-related Vitamin D production. Experimental studies will be needed to determine whether combining hydrotherapy and sunlight may offer immediate hope for all those waiting on a cure.
Note: Please check out the “Comments & Updates” section of this blog – at the bottom of the page. You can find the latest research about this topic there!
To learn more about the studies referenced in today’s column, please click on the following links:
Study 1 – Genetic Risk and a Primary Role for Cell-Mediated Immune … (link)
Study 2 – Hydrotherapy for the Treatment of Pain in People with Multiple … (link)
Study 3 – Community-Based Group Aquatic Program for Individuals with … (link)
Study 4 – Effect of Aquatic Exercise on the Multiple Sclerosis … (link)
Study 5 – Sun Exposure and Vitamin D are Independent Risk Factors … (link)
Study 6 – Association of UV Radiation with Multiple Sclerosis … (link)
Study 7 – Sun Exposure, Vitamin D and Age at Disease Onset … (link)
Hydrotherapy May Improve Quality of Life in MS Patients
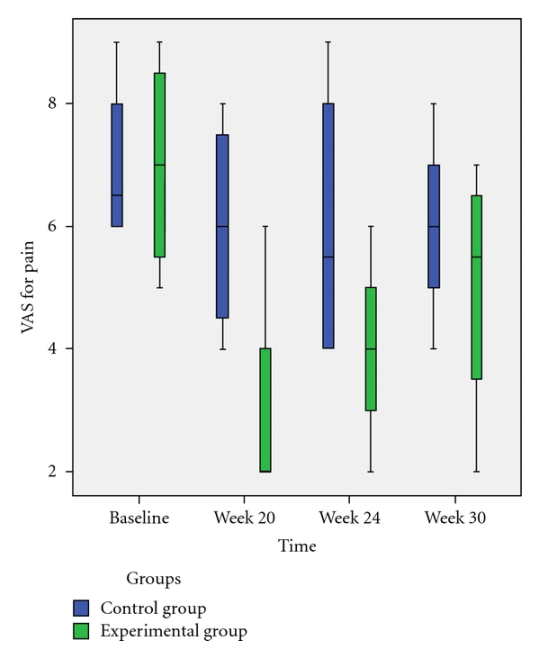
Source: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012: 473963. (link)
Tags: Hydrotherapy, Multiple Sclerosis, Water
Posted in Alternative Therapies, Exercise, Mental Health

October 1st, 2011 at 12:36 am
I just wanted to repost a tweet here that may be relevant to anyone reading this with MS:
http://today.uci.edu/news/2011/09/nr_ms_110930.php
Be well!
JP
August 24th, 2013 at 9:45 pm
I moved to Hawaii in 1977 from Michigan. In my late 40’s I got optical neuritis and an MRI…then went into denial of the RX – MS.
My last 5 years have been pretty much down hill… stabilized with a new MRI and Spinal Tap…ok, still MS. I have ‘AIRBORNE’ usage as my blame for the O.N., and Stress for the last few years… I would love to be questioned, give blood, part of a study *won’t take any drugs though, to be part of a cure, understanding…
August 25th, 2013 at 1:56 pm
Hi Chelle,
You may be able to find a local, clinical trial to participate in here:
http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/search
Also, please search my site and Twitter feed (https://twitter.com/HealthyFellow) for additional information about natural alternatives for MS. I cover the topic on a regular basis. Here are a few examples:
https://www.healthyfellow.com/534/belly-fat-depression-and-multiple-sclerosis-questions/
https://www.healthyfellow.com/899/going-gluten-free/
https://www.healthyfellow.com/394/acupressure-and-massage-news/
Be well!
JP
February 27th, 2015 at 1:17 pm
Update: Coffee use may confer protection against MS …
http://medicalxpress.com/news/2015-02-coffee-multiple-sclerosis.html
“People who drink four to six cups of coffee daily may be less likely to get multiple sclerosis, according to international research out Thursday.
“Caffeine intake has been associated with a reduced risk of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases,” said lead author Ellen Mowry of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland.
“Our study shows that coffee intake may also protect against MS, supporting the idea that the drug may have protective effects for the brain,” she added.
The findings of a US and Swedish study—released ahead of the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting in Washington—each compared more than 1,000 MS patients to a similar number of healthy people.”
Be well!
JP
March 19th, 2015 at 12:50 pm
Update: Hydrotherapy also benefits patients living with fibromyalgia …
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25786047
Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Mar-Apr;33 Suppl 88(1):73-81. Epub 2015 Mar 18.
Effects of a hydrotherapy programme on symbolic and complexity dynamics of heart rate variability and aerobic capacity in fibromyalgia patients.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the effects of a hydrotherapy programme on aerobic capacity and linear and non-linear dynamics of heart rate variability (HRV) in women with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS).
METHODS: 20 women with FMS and 20 healthy controls (HC) took part in the study. The FMS group was evaluated at baseline and after a 16-week hydrotherapy programme. All participants underwent cardiopulmonary exercise testing on a cycle ergometer and RR intervals recording in supine and standing positions. The HRV was analysed by linear and non-linear methods. The current level of pain, the tender points, the pressure pain threshold and the impact of FMS on quality of life were assessed.
RESULTS: The FMS patients presented higher cardiac sympathetic modulation, lower vagal modulation and lower complexity of HRV in supine position than the HC. Only the HC decreased the complexity indices of HRV during orthostatic stimulus. After a 16-week hydrotherapy programme, the FMS patients increased aerobic capacity, decreased cardiac sympathetic modulation and increased vagal modulation and complexity dynamics of HRV in supine. The FMS patients also improved their cardiac autonomic adjustments to the orthostatic stimulus. Associations between improvements in non-linear dynamics of HRV and improvements in pain and in the impact of FMS on quality of life were found.
CONCLUSIONS: A 16-week hydrotherapy programme proved to be effective in ameliorating symptoms, aerobic functional capacity and cardiac autonomic control in FMS patients. Improvements in the non-linear dynamics of HRV were related to improvements in pain and in the impact of FMS on quality of life.
Be well!
JP
April 20th, 2015 at 11:25 am
Udpate 04/17/15:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4387643/
Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2015 Mar-Apr;20(2):200-4.
Comparing the effects of reflexology and relaxation on fatigue in women with multiple sclerosis.
BACKGROUND: Fatigue is the most common and highly disabling symptom of multiple sclerosis (MS) that has negative effects on employment, the process of socialization, compliance with the disease, and other factors effective on activities of daily living. The usage of complementary and alternative medicine methods in MS patients is higher than in the general population. However, there is no scientific evidence to support their effectiveness. Therefore, this study aimed to compare the effects of reflexology and relaxation on fatigue in women with MS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study is a single-blinded randomized clinical trial that was done on 75 patients with MS who referred to the MS Clinic of Ayatollah Kashani Hospital (Isfahan, Iran). After simple non-random sampling, participants were randomly assigned by minimization method to three groups: Reflexology, relaxation, and control groups (25 patients in each group). In the experimental groups, the interventions foot reflexology and relaxation (Jacobson and Benson) were performed for 4 weeks, twice a week for 40 min in each session, and the control group received care and routine medical treatment as directed by a physician. Data were collected through a questionnaire and the fatigue severity scale before, immediately after, and 2 months after interventions from all three groups. Data analysis was performed by SPSS version 18 using descriptive and inferential statistical methods.
RESULTS: Findings obtained from analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that there was no significant difference in the mean fatigue severity scores in the pre-interventions between the three groups (P > 0.05), but there was significant difference immediately after and 2 months after interventions between the three groups (P < 0.05). Findings obtained from repeated measures (ANOVA) showed that there was significant difference in the mean fatigue severity scores during different times between the three groups (P < 0.05), while this difference was not significant in the control group (P > 0.05). Furthermore, least significant difference post-hoc test revealed that the mean scores of fatigue severity immediately after intervention was lower in the reflexology group than in the other two groups and were lower in the relaxation group than in the control group; 2 months after interventions, the mean scores of fatigue severity were lower in the reflexology group than in the other two groups, but there was no significant difference between the two groups of relaxation and control (P > 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: It seems that both interventions were effective in reducing fatigue, but the effects of reflexology on reducing fatigue were more than those of relaxation. Hence, as these two methods are effective and affordable techniques, they can be recommended.
Be well!
JP
July 16th, 2015 at 9:04 pm
Updated 07/16/15:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26157723
Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015 Apr 22;29:205.
The effect of exercise therapy on cognitive functions in multiple sclerosis patients: A pilot study.
BACKGROUND: The positive impacts of exercise therapy on patients’ cognitive problems still remain unknown. This study was a pilot intervention to examine the effects of combined exercise on the cognitive problems of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) in Iranian MS Society over 2012 to 2013.
METHODS: This quasi-experimental research was carried out in the form of a pretest/posttest study. Forty two patients with MS were selected from those visiting the rehabilitation center of Iranian MS Society, using non-probability convenience sampling. The Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) of each patient was recorded before the intervention and Brief Repeatable Battery of Neuropsychological (BRB-N) test was administered before and after the intervention. The data were analyzed using the analytical tests such as Wilcoxon test.
RESULTS: Of 21 participants, 17 subjects (82%, n=14) female with mean (±SD) age of 37 (±9.98) years and mean (±SD) EDSS of 2.35 (±0.90) completed all stages of the study. Changes in long-term storage and permanent long-term retrieval of information after the intervention were statistically significant (p<0.001). In addition, the change in the average of total delay after the intervention was also significant by 1.11 (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION: Our study confirmed the possibility of change in the cognitive abilities of MS patients through physical interventions. This finding emphasizes the necessity of more clinical examinations and increases the hopes for new rehabilitation methods for the disorder.
Be well!
JP
July 23rd, 2015 at 12:57 pm
Updated 07/23/15:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26198928
J Neuroimmunol. 2015 Aug 15;285:125-8.
Effect of high dose vitamin D intake on interleukin-17 levels in multiple sclerosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
BACKGROUND: Vitamin D has immunomodulatory effects in multiple sclerosis (MS). Vitamin D acts through various mechanisms such as secretion of cytokines. Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a critical interleukin in inflammatory response in MS.
OBJECTIVE: This study assessed the effect of oral high dose vitamin D intake on IL-17 levels in MS patients in a double blind randomized clinical trial.
METHODS: 94 patients with a diagnosis of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) were randomized to two groups. One group received 50,000 IU vitamin D3 every five days for 12weeks. The other group was given placebo. Both groups received interferon-β (IFN-β) treatment. Serum levels of IL-17 were measured at the beginning of the study and after 12weeks.
RESULTS: IL-17 serum levels were 56.75±28.72pg/ml and 30.31±75.85pg/ml in the intervention and placebo group at the beginning of the study, respectively (Median±IQR, p=0.338). After 12weeks, IL-17 levels were 58.93±67.93pg/ml and 46.13±94.70pg/ml in the intervention and placebo group, respectively (Median±IQR, p=0.960). The multiple linear regression analysis indicated that the consumption of vitamin D3 was positively and significantly associated with the logarithm of IL-17 measures (β=1.719; p=0.002 and R2=0.91), adjusted by EDSS scores.
CONCLUSION: IL-17 levels showed significant change in RRMS patients after receiving high dose vitamin D3 for 12weeks.
Be well!
JP
July 30th, 2015 at 8:13 pm
Updated 07/30/15:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26223004
J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015 Jul 29.
Influence of yoga and aerobics exercise on fatigue, pain and psychosocial status in patients with multiple sclerosis: A Randomized Trial.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease involving brain and spinal cord. Weakness, cognitive impairment, pain, depression and fatigue, as common symptoms of MS, may significantly affect on general health of MS patients. This study aimed to investigate the influence of yoga and aerobic exercise on fatigue, pain, and psychosocial status among these patients.
METHODS: In a randomized clinical trial study on 90 patients whom were randomly assigned to three equal groups of yoga exercises, aerobics exercises, and control group. The exercise program was performed as three sessions per week for 12 weeks. The exercise program included 40 minutes, including 5-10 minutes for warm-up, 25-30 minutes of exercise (walking), and 5 minutes for cooling down. Yoga exercises were scheduled three sessions a week for 12 weeks as well.
RESULTS: There was no significant difference in fatigue, pain severity and psychological status among three groups prior to the study, but after the study, in yoga and exercise groups, fatigue physical function, physical and emotional role which patients play throughout daily life, social function, energy, mental status and overall hygiene increased, and the pain and fatigue were relieved in the patients.
CONCLUSION: Yoga and aerobics exercise could decrease some of the MS symptoms, therapeutic costs, hospital stay, and days lost from work as well as increasing the patients’ efficiency.
Be well!
JP
August 6th, 2015 at 2:44 pm
Updated 08/06/15:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26243188
BMC Neurol. 2015 Aug 5;15:132.
Latitude, sun exposure and vitamin D supplementation: associations with quality of life and disease outcomes in a large international cohort of people with multiple sclerosis.
BACKGROUND: A growing evidence base implicates vitamin D, sun exposure and latitude in the aetiology of multiple sclerosis (MS), however there are less data on the associations of these variables with disease outcomes.
METHODS: We undertook a cross-sectional survey of over 2000 people with MS recruited through internet platforms, seeking self-reported data on geographical location, intentional sun exposure for health, and supplementation with vitamin D, among other lifestyle variables. We also requested data on health-related quality of life (MSQOL-54), self-reported doctor-diagnosed relapse rate, and disability (Patient Determined Disease Steps). Bivariate and multivariate analyses were used for comparisons, including multiple linear regression modeling.
RESULTS: Of 2301 participants, 82.3 % were female, median age was 45 years (IQR 38-53 years), with a median time since diagnosis of 6 years (IQR 3-12 years), the majority (61.6 %) having relapsing-remitting MS. Nearly two-thirds (64.6 %) lived in the Northern hemisphere, mostly in developed countries. Most (66.8 %) reported deliberate sun exposure to raise their vitamin D level, and the vast majority (81.8 %) took vitamin D supplements, mostly 2000-5000 IU a day on average. Unadjusted regression modeling incorporating deliberate sun exposure, latitude and vitamin D supplementation showed strong associations of sun exposure with HRQOL which disappeared when controlling for gender, age, disability, physical activity, and fish consumption. In contrast, associations between vitamin D supplementation and HRQOL were maintained adjusting for these variables, with a dose-response effect. Only latitude had significant adjusted associations with disability, with an increase of latitude by one degree (further from the equator) predicting increased odds of moderate disability (OR 1.02 (95 % CI 1.01-1.04)) or high disability (OR 1.03 (95 % CI 1.01-1.05)) compared to no/mild disability. Similarly, latitude was related to relapse rate, with increase in latitude of 1 degree associated with increased odds of having more relapses over the previous year (1.01 (1.00-1.02)).
CONCLUSIONS: We detected significant associations between latitude, deliberate sun exposure and vitamin D supplementation and health outcomes of this large group of people with MS. Vitamin D is likely to have a key role in these associations and its role in the health outcomes of people with MS urgently requires further study.
Be well!
JP
September 14th, 2015 at 3:33 pm
Updated 09/14/15:
http://msj.sagepub.com/content/early/2015/08/20/1352458515604380.abstract
Mult Scler. 2015 Sep 11.
Higher intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is associated with a decreased risk of a first clinical diagnosis of central nervous system demyelination: Results from the Ausimmune Study.
BACKGROUND: There is contradictory evidence for a role of dietary fat in risk of multiple sclerosis (MS).
OBJECTIVES: To examine the association between usual fat intake (total, saturated, monounsaturated (MUFA), polyunsaturated (PUFA), omega-3 and omega-6) and risk of a first clinical diagnosis of CNS demyelination (FCD).
METHODS: Multi-centre incident case-control study in four regions of Australia during 2003-2006. Cases were aged 18-59 years and had a FCD; controls were matched to a case on age, sex and location. Dietary data were collected using a validated food frequency questionnaire.
RESULTS: In 267 cases and 517 controls with dietary data, higher intake (per g/day) of omega-3 PUFA (adjusted odds ratio, AOR=0.61 (95% CI 0.40-0.93)), and particularly that derived from fish (AOR=0.54 (95% CI 0.31-0.93)) rather than from plants (AOR=0.75 (95% CI 0.39-1.43)) was associated with a decreased risk of FCD. Total fat intake and intake of other types of fat were not associated with FCD risk.
CONCLUSIONS: There was a significant decrease in FCD risk with higher intake of omega-3 PUFA, particularly that originating from fish. There was no evidence to indicate that the intake of other types of dietary fat or fat quantity in the previous 12 months was associated with an altered risk of FCD.
Be well!
JP
December 23rd, 2015 at 12:19 am
Updated 12/22/15:
http://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=9000&issue=00000&article=97641&type=abstract
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Dec 11.
Exercising Impacts on Fatigue, Depression, and Paresthesia in Female Patients with MS.
PURPOSE: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic progressive autoimmune disease impacting both body and mind. Typically, patients with MS report fatigue, depression and paresthesia. Standard treatment consists of immune modulatory medication, though there is growing evidence that exercising programs have a positive influence on fatigue and psychological symptoms such as depression. We tested the hypothesis that, as in addition to the standard immune regulatory medication, either yoga or aquatic exercise can ameliorate both fatigue and depression, and we examined whether these interventions also influence paresthesia compared to a non-exercise control condition.
METHODS: Fifty-four women with MS (mean age: M=33.94 years, SD=6.92) were randomly assigned to one of the following conditions: yoga; aquatic exercise; non-exercise control. Their existing immune modulatory therapy remained unchanged. Participants completed questionnaires covering symptoms of fatigue, depression, and paresthesia, both at baseline and on completion of the study eight weeks later.
RESULTS: Compared to the non-exercise control condition and over time, fatigue, depression, and paresthesia decreased significantly in the yoga and aquatic exercise groups. On study completion, the likelihood of reporting moderate to severe depression was 35-fold higher in the non-exercise control condition than in the intervention conditions (yoga and aquatic exercising values collapsed).
CONCLUSION: The pattern of results suggests that for females with MS and treated with standard immune regulatory medication, exercise training programs such as yoga and aquatic exercising positively impacts on core symptoms of MS, namely fatigue, depression, and paresthesia. Exercise training programs should be considered in the future as possible complements to standard treatments.
Be well!
JP
March 30th, 2016 at 6:05 pm
Updated 03/30/16:
http://ijaai.tums.ac.ir/index.php/ijaai/article/view/692
Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016 Feb;15(1):13-9.
Effect of Vitamin A Supplementation on fatigue and depression in Multiple Sclerosis patients: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
Decreasing the population and activation of inflammatory T helper cells in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients using vitamin A derivatives (retinoic acids) has been well documented. The present study determined the effect of vitamin A supplementation on psychiatric signs in MS patients. The subjects were 101 relapsing-remitting MS patients enrolled in a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. The treatment group was administered 25000 IU/d retinyl palmitate (RP) for 6 months followed by 10000 IU/d RP for another 6 months. The results for baseline characteristics, modified fatigue impact scale and Beck Depression Inventory-II were recorded at the beginning and end of the one-year study. The non-normal distribution data was compared between groups using a nonparametric test and normal distribution data was analyzed using a parametric test. (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: NCT01417273). The results showed significant improvement in the treatment group for fatigue (p=0.004) and depression (p=0.01). Vitamin A supplementation helped during interferon therapy in the treatment process and improved psychiatric outcomes for anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Be well!
JP
June 3rd, 2016 at 11:31 am
Updated 06/03/16:
http://www.msard-journal.com/article/S2211-0348%2816%2930029-3/abstract
Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2016 May;7:70-3.
Effects of Pilates exercises on sensory interaction, postural control and fatigue in patients with multiple sclerosis.
BACKGROUND: Decreased postural control, sensory integration deficits and fatigue are important problems that cause functional impairments in patients with multiple sclerosis (pwMS).
PURPOSE: To examine the effect of modified clinical Pilates exercises on sensory interaction and balance, postural control and fatigue in pwMS.
METHODS: Eleven patients with multiple sclerosis and 12 healthy matched controls were recruited in this study. Limits of stability and postural stability tests were used to evaluate postural control by Biodex Balance System and sensory interaction assessed. Fatigue was assessed by Modified Fatigue Impact Scale. Pilates exercises were applied two times a week for 10 weeks and measurements were repeated to pwMS after exercise training.
RESULTS: Postural control and fatigue (except psychosocial parameter) of pwMS were significantly worser than healthy controls (p<0.05). Significant improvements occurred in sensory interaction (eyes open, foam surface) and total, physical and cognitive scores of fatigue after 10-week modified clinical Pilates training (p<0.05). No significant changes were detected in postural control after the pilates exercises (p>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: Ten-week Pilates training is effective to improve sensory interaction and to decrease fatigue. Pilates exercises can be applied safely in ambulatory pwMS for enhance sensory interaction and balance and combat fatigue. More investigations are needed.
Be well!
JP
June 15th, 2016 at 1:35 pm
Updated 06/15/16:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09540261.2016.1191447?journalCode=iirp20
Int Rev Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 14:1-10.
Immediate effect of two yoga-based relaxation techniques on cognitive functions in patients suffering from relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: A comparative study.
Cognitive impairment (CI) is an important feature of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Yogic relaxation techniques have been found useful in improving various cognitive domains in health and disease. Eighteen subjects (13 females) in the age range of 51.5 ± 12.72 years with the diagnosis of RRMS by a neurologist (McDonald Criteria 2010) since last 18.16 ± 12.59 years were recruited into the study from a neuro-rehabilitation centre in Germany. Assessments were done before and immediately after two randomly allocated 30-min sessions of yogic relaxation: Cyclic Meditation (CM) and SR (supine rest or shavasana). Assessments were done for attention, psychomotor performance, information processing speed, executive functions, and immediate and delayed recall using standard psychometric tools. RMANOVA was applied to analyse the data using SPSS version 10. Both CM and SR sessions improved scores on Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) (p < 0.01) and Auditory Verbal Learning Test (AVLT) (p < 0.05). There was a significantly better performance in Trail Making Test (TMT)-A and forward digit span (FDS) after CM as compared to SR (p < 0.01). Yogic relaxation techniques may have an immediate enhancing effect on processing speed, psychomotor performance, and recall of RRMS patients. CM is better than SR in improving processing speed, short-term memory, and verbal working memory. Be well! JP
June 26th, 2016 at 6:55 pm
Updated 06/26/16:
http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/jcim.ahead-of-print/jcim-2015-0105/jcim-2015-0105.xml
J Complement Integr Med. 2016 Jun 23.
Effect of integrated Yoga and Physical therapy on audiovisual reaction time, anxiety and depression in patients with chronic multiple sclerosis: a pilot study.
BACKGROUND: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is characterized by a significant deterioration in auditory and visual reaction times along with associated depression and anxiety. Yoga and Physical therapy (PT) interventions have been found to enhance recovery from these problems in various neuropsychiatric illnesses, but sufficient evidence is lacking in chronic MS population. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of integrated Yoga and Physical therapy (IYP) on audiovisual reaction times, depression and anxiety in patients suffering from chronic MS.
METHODS: From a neuro-rehabilitation center in Germany, 11 patients (six females) suffering from MS for 19±7.4 years were recruited. Subjects were in the age range of 55.45±10.02 years and had Extended Disability Status Scores (EDSS) below 7. All the subjects received mind-body intervention of integrated Yoga and Physical therapy (IYP) for 3 weeks. The intervention was given in a residential setup. Patients followed a routine involving Yogic physical postures, pranayama, and meditations along with various Physical therapy (PT) techniques for 21 days, 5 days a week, 5 h/day. They were assessed before and after intervention for changes in audiovisual reaction times (using Brain Fit Model No. OT 400), anxiety, and depression [using Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS)]. Data was analyzed using paired samples test.
RESULTS: There was significant improvement in visual reaction time (p=0.01), depression (p=0.04), and anxiety (p=0.02) scores at the end of 3 weeks as compared to the baseline. Auditory reaction time showed reduction with borderline statistical significance (p=0.058).
CONCLUSIONS: This pilot project suggests utility of IYP intervention for improving audiovisual reaction times and psychological health in chronic MS patients. In future, randomized controlled trials with larger sample size should be performed to confirm these findings.
Be well!
JP
September 7th, 2016 at 12:19 pm
Updated 09/07/16:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01616412.2016.1227913?journalCode=yner20
Neurol Res. 2016 Sep 6:1-5.
High dose Vitamin D intake and quality of life in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
BACKGROUND: Low level of vitamin D is associated with a more severe course and low quality of life in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Low dose vitamin D intake has improved quality of life in RRMS patients.
OBJECTIVE: This study explored the effect of high dose vitamin D intake on quality of life in RRMS patients in a double blind randomized clinical trial.
METHODS: 94 RRMS patients were randomized to two groups. One group received 50,000 IU vitamin D3 every five days for 3 months. The other group received placebo. Interferon-β (IFN-β) continued as the main treatment in both groups. Quality of life was assessed using MSQOL-54 Persian version at the beginning and at the end of the study.
RESULTS: After 3 months, the vitamin D group had a significant difference in mental health composite with placebo group, 62.41 ± 13.99 vs. 60.99 ± 17.99 (p-value = 0.041). Change in health was 75.74 ± 25.73 and 70.59 ± 26.45 in vitamin D and placebo group, respectively (p-value = 0.036).
CONCLUSIONS: Mental QOL improved significantly after taking high dose vitamin D for 3 months in vitamin D group relative to placebo.
Be well!
JP
September 15th, 2016 at 6:18 pm
Updated 09/15/16:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4963747/
J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Jun;10(6):VC01-VC05.
Effects of Yoga on Physiological Indices, Anxiety and Social Functioning in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Randomized Trial.
INTRODUCTION: Multiple sclerosis (MS) as a chronic disease could affect patients’ various domains of life.
AIM: This study was conducted to study the effect of yoga on the physiological indices, anxiety and social functioning of patients with MS in southwest, Iran.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this clinical trial study, 60 MS patients were enrolled according to inclusion criteria and randomly assigned to two groups of 30 each. Prior to and after intervention, the patients’ vital signs were measured. For case group yoga exercises were performed three sessions a week for 12 weeks while control group performed no exercise. The data were gathered by questionnaire and analysed by descriptive and analytical statistics in SPSS.
RESULTS: Prior to intervention, there was no significant difference in fatigue severity and pain between the two groups but the mean fatigue severity and pain in case group decreased compared to the control group after the intervention. Prior to intervention, there was no significant difference in mean physiological indices between the two groups but the mean physiological indices in case group decreased significantly after the intervention (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION: Yoga is likely to increase self-efficacy of MS patients through enhancing physical activity, increasing the strength of lower limbs and balance, and decreasing fatigue and pain, and finally to promote social functioning and to relieve stress and anxiety in these patients.
Be well!
JP
September 22nd, 2016 at 10:51 pm
Updated 09/22/16:
http://www.msard-journal.com/article/S2211-0348(16)30100-6/fulltext
Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2016 Sep;9:80-90.
Low-fat, plant-based diet in multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial.
BACKGROUND: The role that dietary interventions can play in multiple sclerosis (MS) management is of huge interest amongst patients and researchers but data evaluating this is limited. Possible effects of a very-low-fat, plant-based dietary intervention on MS related progression and disease activity as measured by brain imaging and MS related symptoms have not been evaluated in a randomized-controlled trial. Despite use of disease modifying therapies (DMT), poor quality of life (QOL) in MS patients can be a significant problem with fatigue being one of the common disabling symptoms. Effective treatment options for fatigue remain limited. Emerging evidence suggests diet and vascular risk factors including obesity and hyperlipidemia may influence MS disease progression and improve QOL.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate adherence, safety and effects of a very-low-fat, plant-based diet (Diet) on brain MRI, clinical [MS relapses and disability, body mass index (BMI)] and metabolic (blood lipids and insulin) outcomes, QOL [Short Form-36 (SF-36)], and fatigue [Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) and Modified Fatigue Impact Scale (MFIS)], in relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS).
METHODS: This was a randomized-controlled, assessor-blinded, one-year long study with 61 participants assigned to either Diet (N=32) or wait-listed (Control, N=29) group.
RESULTS: The mean age (years) [Control-40.9±8.48; Diet-40.8±8.86] and the mean disease duration (years) [Control -5.3±3.86; Diet-5.33±3.63] were comparable between the two groups. There was a slight difference between the two study groups in the baseline mean expanded disability status scale (EDSS) score [Control-2.22±0.90; Diet-2.72±1.05]. Eight subjects withdrew (Diet, N=6; Control, N=2). Adherence to the study diet based on monthly Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) was excellent with the diet group showing significant difference in the total fat caloric intake compared to the control group [total fat intake/total calories averaged ~15% (Diet) versus ~40% (Control)]. The two groups showed no differences in brain MRI outcomes, number of MS relapses or disability at 12 months. The diet group showed improvements at six months in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (Δ=-11.99mg/dL; p=0.031), total cholesterol (Δ=-13.18mg/dL; p=0.027) and insulin (Δ=-2.82mg/dL; p=0.0067), mean monthly reductions in BMI (Rate=-1.125kg/m2 per month; p<0.001) and fatigue [FSS (Rate=-0.0639 points/month; p=0.0010); MFIS (Rate=-0.233 points/month; p=0.0011)] during the 12-month period.
CONCLUSIONS: While a very-low fat, plant-based diet was well adhered to and tolerated, it resulted in no significant improvement on brain MRI, relapse rate or disability as assessed by EDSS scores in subjects with RRMS over one year. The diet group however showed significant improvements in measures of fatigue, BMI and metabolic biomarkers. The study was powered to detect only very large effects on MRI activity so smaller but clinically meaningful effects cannot be excluded. The diet intervention resulted in a beneficial effect on the self-reported outcome of fatigue but these results should be interpreted cautiously as a wait-list control group may not completely control for a placebo effect and there was a baseline imbalance on fatigue scores between the groups. If maintained, the improved lipid profile and BMI could yield long-term vascular health benefits. Longer studies with larger sample sizes are needed to better understand the long-term health benefits of this diet.
Be well!
JP
January 20th, 2017 at 9:26 pm
Updated 01/20/17:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01616412.2016.1227913?journalCode=yner20
Neurol Res. 2016 Oct;38(10):888-92.
High dose Vitamin D intake and quality of life in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
BACKGROUND: Low level of vitamin D is associated with a more severe course and low quality of life in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Low dose vitamin D intake has improved quality of life in RRMS patients.
OBJECTIVE: This study explored the effect of high dose vitamin D intake on quality of life in RRMS patients in a double blind randomized clinical trial.
METHODS: 94 RRMS patients were randomized to two groups. One group received 50,000 IU vitamin D3 every five days for 3 months. The other group received placebo. Interferon-β (IFN-β) continued as the main treatment in both groups. Quality of life was assessed using MSQOL-54 Persian version at the beginning and at the end of the study.
RESULTS: After 3 months, the vitamin D group had a significant difference in mental health composite with placebo group, 62.41 ± 13.99 vs. 60.99 ± 17.99 (p-value = 0.041). Change in health was 75.74 ± 25.73 and 70.59 ± 26.45 in vitamin D and placebo group, respectively (p-value = 0.036).
CONCLUSIONS: Mental QOL improved significantly after taking high dose vitamin D for 3 months in vitamin D group relative to placebo.
Be well!
JP
January 29th, 2017 at 5:38 pm
Updated 01/29/17:
http://www.ctcpjournal.com/article/S1744-3881(16)30177-3/fulltext
Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Feb;26:21-25.
The effect of yoga training on enhancement of Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol levels in female patients with multiple sclerosis.
The effect of 8 weeks yoga training on cortisol and Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels in female patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is examined. Twenty four MS female patients with Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) 1 to 5.5 participated in this study as the subject. The participants were divided into control (n = 10) or training group (n = 14) randomly. Training group performed 90 min yoga training per session, 3 days a week for 8 weeks. Assessments include body composition measurement and blood sampling 48 h before first session and 48 h after the intervention. The results demonstrated that ACTH increased and cortisol decreased compared to the control group (P < 0.05); In conclusion, it seems that yoga training modulates ACTH level in concomitant with reduction in cortisol level in female patients with MS. Be well! JP
November 5th, 2017 at 8:49 pm
Updated 11/05/17:
http://ijmsc.org/doi/10.7224/1537-2073.2015-095?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&code=cmsc-site
Int J MS Care. 2017 Sep-Oct;19(5):225-231.
Mindfulness in Motion for People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Feasibility Study.
BACKGROUND: Mindfulness in Motion is an 8-week mindfulness-based intervention that uses yoga movement, mindfulness meditation, and relaxing music. This study examined the feasibility of using Mindfulness in Motion in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) and the effect of this program on stress, anxiety, depression, fatigue, and quality of life in people with MS.
METHODS: Twenty-two people with MS completed the 8-week mindfulness program as well as assessments 1 week before and after the intervention.
RESULTS: Pre/post comparison of four self-reported questionnaires-the Mental Health Inventory, 36-item Short Form Health Status Survey, Modified Fatigue Impact Scale, and Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire-showed significant improvement in physical functioning, vitality, and mental health. Specifically, improvements were seen in anxiety, depression, and positive affect; cognitive, psychosocial, and overall functioning regarding fatigue; and mindfulness in the areas of observing, acting with awareness, nonjudgment, and nonreactivity.
CONCLUSIONS: Due to the uncertainty in disease progression associated with MS, and the multiplicity of mental and physical symptoms associated with it, programming that addresses anxiety, depression, and fatigue is a key area of future research in MS disease management. Mindfulness in Motion proved to be a feasible program yielding positive results, supporting the need for research to determine the extent to which the program can improve quality-of-life outcomes for people with MS.
Be well!
JP
December 18th, 2017 at 6:14 pm
I am a 64 year old female, I was diagnosed of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in 2008 (MRI), my symptoms started out with severe fatigue, poor balance, numbness, double vision, heat intolerance and anxiety. I was unable to go back to work, I tried Betaseron for about 6 years. Tried every shot available, all made me sick.
In November 2015, I started on Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Herbal formula from NewLife Clinic, the treatment worked incredibly for my MS condition. I used the NewLife MS Herbal formula for a total time period of 4 months, it totally reversed my Multiple Sclerosis. I had a total decline of all symptoms including vision problems, numbness and others. Sometimes, i totally forget i ever had MS.
Visit NewLife Clinic. I am very pleased with this treatment. I eat well, sleep well and exercise regularly. My attitude is extremely positive.
June 22nd, 2018 at 12:20 pm
Updated 06/22/18:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29928122
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018 Jun 12;14:1505-1512.
The effect of evening primrose oil on fatigue and quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Background: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic progressive and inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that is characterized by demyelination in the central nervous system. In regard to the prevalence of diseases and enormous costs imposed on society and the health system, finding a way to stop the progression of the disease using drugs with fewer side effects seems a serious sanitation issue to the health of the international community. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of evening primrose oil (EPO) on fatigue and quality of life in patients with MS.
Materials and methods: In this double-blind randomized clinical trial, 52 patients with MS were chosen and categorized into 2 groups which received 2 doses of EPO and placebo. In addition, the quality of life and fatigue scale in these patients were investigated before the treatment and again 3 months after therapy. The findings were then compared between the 2 groups.
Result: EPO consumption significantly increased cognitive function, vitality, and overall life satisfaction and also reduced pain and fatigue compared to placebo (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that EPO consumption had no impact on the quality of life in general; however, it had a significant effect on several important aspects of life quality such as the increase of cognitive function, vitality, and overall life satisfaction. It also reduced the pain and fatigue in comparison to the placebo consumption. Herbal medicines are brittle and have fewer side effects than chemical drugs. With use of this plant, reduced fatigue and improved quality of life were observed in MS patients. But the drug did not prevent the progression of the disease.
Be well!
JP
January 8th, 2019 at 2:41 pm
Updated 01/08/19:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711318302034?via%3Dihub
Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:89-97.
Achillea millefolium is beneficial as an add-on therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial.
BACKGROUND: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disease for which to date there is no cure and the existing disease-modifying drugs just slow down the disease progression.
PURPOSE: In this clinical trial we evaluated the efficacy of Achillea millefolium (A. millefolium) aqueous extract in MS patients.
METHODS: A triple-blind randomized placebo-controlled parallel group trial was conducted on 75 MS patients. The patients were randomized into three groups including placebo and two groups receiving A. millefolium with two different doses, i.e. 250 mg/day and 500 mg/day, for 1 year. The primary outcome was the annualized relapse rate. Also, number and volume of lesions were obtained from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Furthermore, we performed a comprehensive neurological and cognitive tests as follows: changes in the expanded disability status scale (EDSS), the multiple sclerosis functional composite (MSFC), fatigue severity scale (FSS), Ashworth spasticity assessment, Beck depression test, State-trait anxiety inventory (STAI), mini-mental status examination (MMSE), Wisconsin card sorting test (WCST), tower of London test (TOL), word-pair learning, paced auditory serial addition task (PASAT) and standard laboratory tests.
RESULTS: This study showed one year administration of A. millefolium (both doses) decreased the annual relapse rate in MS patients. The mean volume change of lesions significantly decreased in the 500 mg A. millefolium group. The add-on therapy also increased time to first relapse and the MSFC z-score; it decreased the EDSS score and improved performance in word-pair learning, PASAT, and WCST.
CONCLUSION: We found beneficial effects of A. millefolium aqueous extract as an add-on therapy in MS patients.
Be well!
JP
June 2nd, 2019 at 8:27 am
Been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis in 2015, and I was a woman of 50. They put me on Rebif which I took until 2017 and was switched to Copaxone. I had two relapses on Rebif, none so far on Copaxone. I do notice my balance was getting worse, and my memory, as well as erectile dysfunction and spasms’ had no choice to sick for other solution and I was introduce to totalcureherbsfoundation c om which I purchase the MS herbal formula from the foundation, the herbal supplement has effectively get rid of my multiple sclerosis and reversed all symptoms.
March 5th, 2021 at 5:15 am
Been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis in 2015, and I was a woman of 50. They put me on Rebif which I took until 2017 and was switched to Copaxone. I had two relapses on Rebif, none so far on Copaxone. I do notice my balance was getting worse, and my memory, i had no choice to sick for other solution and I was introduce to multivitamincare .org which I purchase the MS herbal formula from the org, the herbal supplement has successfully get rid of my multiple sclerosis and reversed all symptoms after using the herbs as the Dr said , this is almost a miracle and do believe multivitamincare .org herbal cure will be recognize globally because am sure the world are yet to see their wonderful work.